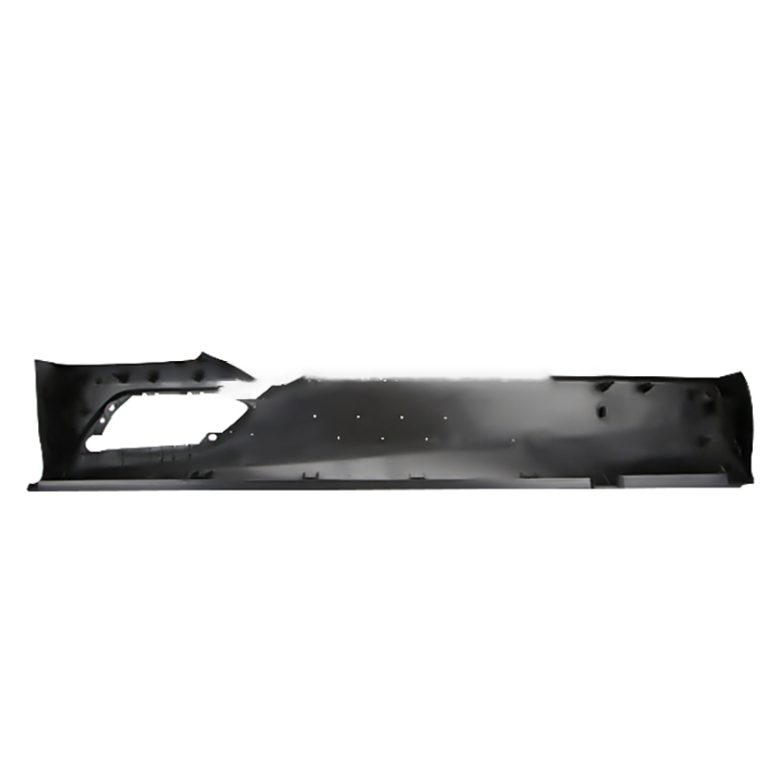
Creating custom plastic parts through ABS injection molding involves several key steps and considerations. Here’s an overview of the process and factors to keep in mind:
- Design Phase
1.CAD Design: Begin with a detailed CAD (Computer-Aided Design) model of your part. This includes dimensions, features, and any specific requirements like tolerances or surface finishes.
2.Design for Manufacturability (DFM): Ensure your design is optimized for injection molding. Consider factors such as draft angles, wall thickness uniformity, and parting lines.
- Prototype Development
3.Prototyping: Before mass production, create prototypes to verify the design and functionality. This helps identify any issues early in the process.
4.3D Printing vs. Injection Molding: For initial prototypes, 3D printing might be cost-effective. However, it may not replicate all properties of the final ABS injection molded part.
- Tooling Design and Fabrication
5.Tooling: Injection molds are typically made from hardened steel. The cost and lead time for tooling can vary based on part complexity and the number of cavities in the mold.
6.Tooling Considerations: Choose between single-cavity molds (cheaper, slower) and multi-cavity molds (more expensive, faster).
- Injection Molding Process
7.Injection Molding Machine: Select a machine suitable for ABS plastic, considering shot size, clamping force, and injection pressure requirements.
8.Material Selection: ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a common thermoplastic known for its strength, impact resistance, and versatility. It’s suitable for a wide range of applications.
9.Injection Molding Steps:
10.Injection: The molten ABS material is injected into the mold cavity under high pressure.
11.Cooling: The mold cools the material, allowing it to solidify and take the shape of the cavity.
12.Ejection: Once cooled, the mold opens, and the part is ejected.
- Post-Processing and Quality Control
13.Trimming and Finishing: Remove any excess material (flash) and perform any necessary post-processing operations (e.g., machining, painting, or assembly).
14.Quality Control: Inspect parts for dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and any defects using tools like coordinate measuring machines (CMM) or visual inspection.
- Production and Scaling
15.Production Run: Once prototypes are approved, begin the full-scale production run. Monitor the process to maintain consistency and quality.
16.Cost Considerations: Factors influencing cost include mold complexity, material selection, part volume, and finishing requirements.
- Supplier Selection
17.Choosing a Manufacturer: Look for a reputable injection molding company with experience in ABS and custom part production. Consider their capabilities, quality assurance processes, and customer reviews.
Considerations for Small Minimum Orders:
18.Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ): Some manufacturers may have minimum order requirements due to setup costs and material waste. Negotiate based on your specific needs.
19.Cost Considerations: Injection molding can have higher initial setup costs but becomes more cost-effective with larger production volumes.
By following these steps and considerations, you can effectively navigate the process of creating custom ABS injection molded plastic parts, even with small minimum orders. Working closely with an experienced manufacturer will ensure your design requirements are met while maintaining quality and cost-efficiency.