In the context of rapid prototyping processes, there’s often confusion between the terms “samples” and “prototypes.” Let’s clarify the differences:
1.Samples:
2.Definition: Samples are typically small-scale representations or examples of a product or component that are produced in a limited quantity and are used primarily for evaluation, testing, or demonstration purposes.
3.Purpose: Samples are created to showcase a particular feature, material, or design aspect of a product. They are not necessarily complete representations of the final product but serve as examples to demonstrate specific characteristics.
4.Production: Samples can be manufactured using various methods, including rapid prototyping techniques, but they are often produced in smaller quantities compared to prototypes.
5.Use: They are commonly used in industries like manufacturing, fashion, and consumer goods to gather feedback, test market acceptance, or demonstrate functionality.
6.Prototypes:

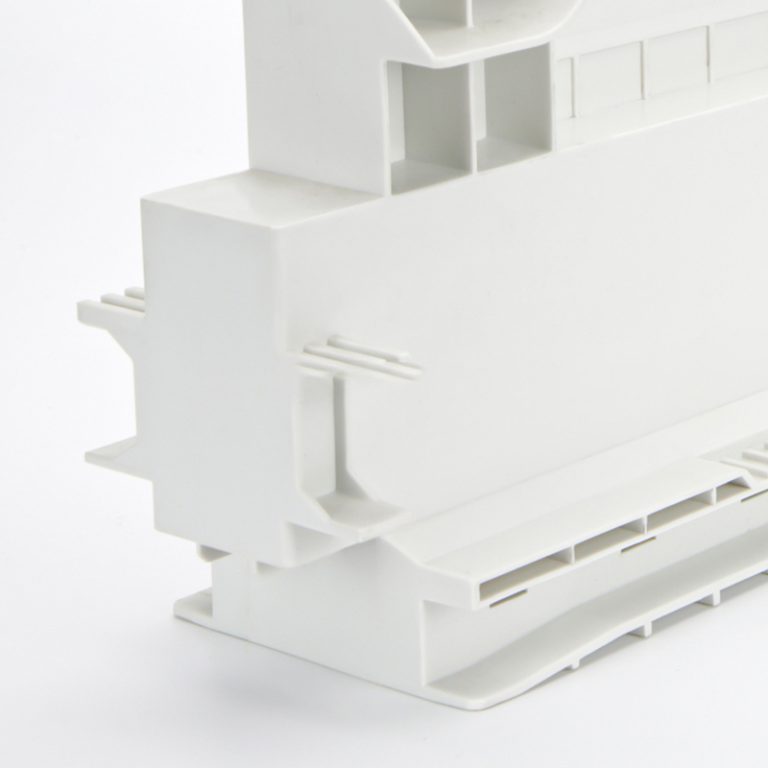
7.Definition: Prototypes are more comprehensive and fully functional representations of a product or component that simulate the final product as closely as possible.
8.Purpose: Prototypes are created to validate the design, functionality, and manufacturability of a product before mass production begins. They allow engineers and designers to test and refine the product’s performance and usability.
9.Production: Prototypes are typically produced using advanced manufacturing technologies such as 3D printing, CNC machining, or injection molding. They can be made from production-grade materials to closely mimic the final product.
10.Use: Prototypes are crucial in the product development lifecycle, helping to identify design flaws, optimize features, and ensure that the product meets quality standards and user expectations.
Key Differences:
11.Scope and Completeness: Samples are partial representations focusing on specific aspects (like material or design feature), whereas prototypes aim to replicate the entire product functionality and appearance.
12.Purpose and Testing: Samples are used for initial evaluation and testing of individual elements, while prototypes undergo comprehensive testing to validate overall design and functionality.
13.Production Methods: Samples can be produced using various methods, including rapid prototyping techniques, whereas prototypes often require more advanced manufacturing processes and materials.
In summary, while both samples and prototypes play important roles in product development, prototypes are more comprehensive, functional, and representative of the final product, whereas samples serve specific purposes such as showcasing features or materials.